What is IBD?
Chronic inflammation of all or part of the digestive tract is commonly called as Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
IBD refers to two diseases of the digestive system, namely Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC).
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are diseases that inflame the lining of the GI (gastrointestinal) tract and disrupt the body's ability to digest food, absorb nutrition, and eliminate waste in a healthy manner.
Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract from mouth to anus, but is usually located in the lower part of the small intestine and the upper colon.
It usually appears in patches. Patches of inflammation are present between healthy portions of the gut.
Crohn's disease can affect all the layers of the bowel (intestinal) wall.
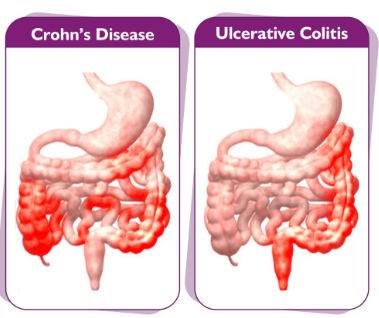
Ulcerative colitis is limited to the large intestine (colon) & rectum.
Ulcerative colitis is continuous inflammation of the colon & rectum. It almost always starts at the rectum, extending upwards in a continuous manner through the colon.
Ulcerative colitis only affects the inner most lining of the intestinal wall.